Replicación del DNA y daño endógeno
Biología del Genoma
Descripción
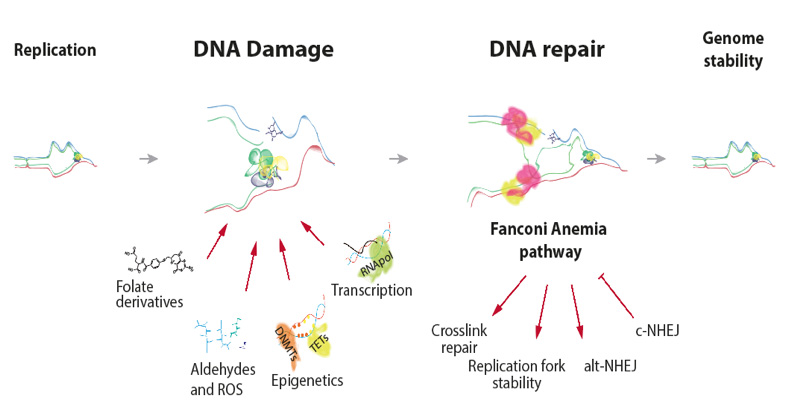
The repair of damaged DNA is of critical importance to ensure the faithful transmission of genetic information from a mother cell to its daughter. To this purpose, cells have evolved several DNA repair pathways that survey, detect and fix DNA lesions, to avoid devastating consequences in humans. One example of these consequences is the Fanconi Anaemia syndrome, an ultrarare genetic instability disease featured by congenital abnormalities, stem cell loss and extreme cancer predisposition, as a consequence of exacerbated genomic instability associated to replication defects. The FA/BRCA repair pathway comprises 22 genes (FANCA to FANCW) so far identified, and is essential for ICL repair during S phase and requires two converging replication forks to the ICL. The Fanconi Anaemia pathway received much attention, when one of the genes, FANCD1, was identified as BRCA2, the most frequently mutated gene in breast and ovarian cancer. Whereas the Fanconi anaemia pathway orchestrates lesion recognition, strand incisions, bypass and strand restoration during ICL repair, some FANC proteins has many other crucial functions such as regulation of the replication fork stability or limiting the formation of toxic DNA:RNA hybrids (R-loops) at transcription replication conflicts (TRCs).
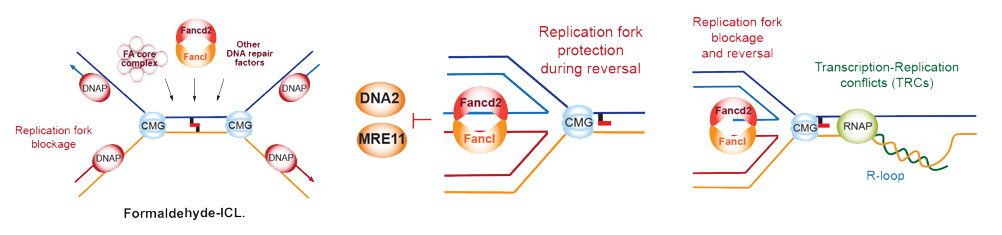
Many chemical and physical agents constantly challenge ongoing DNA replication. The formation of ICLs in DNA can result from exposure to chemical agents that react with nucleobases forming covalent bonds between bases on opposite DNA strands. ICLs are highly cytotoxic DNA lesions as they prevent DNA unwinding during replication, transcription or recombination processes. Our research effort focusses on the identification of metabolic agents endogenously produced during physiological processes that thread replication dynamics, ultimately leading to replication stress. We specially focus on reactive aldehydes (i.e. formaldehyde), a novel and extremely reactive compound produced inside our cells. Formaldehyde chemically modifies DNA bases and proteins. However, aldehydes are also present in our daily routine, as alcohol, cigarette smoke or dietary fat release vast amount of these reactive chemicals, that are now recognized as exogenous source of ICLs. Aldehyde-ICLs are mainly repaired by an incision mechanism coupled to DNA replication carried out by the FA pathway in concert with other repair mechanisms. For this reason, cells evolved a family of enzymes called aldehyde dehydrogenases (EC 1.2.1.3) that catalyses aldehyde oxidation to non-toxic carboxylic acids. The importance of this gene family is revealed by human medical conditions affecting tumour incidence and bone marrow failure like the Fanconi Anaemia, the “Alcohol Flush Reaction” or the recently discovered “Aldehyde Degradation Deficiency (ADD)” síndromes.
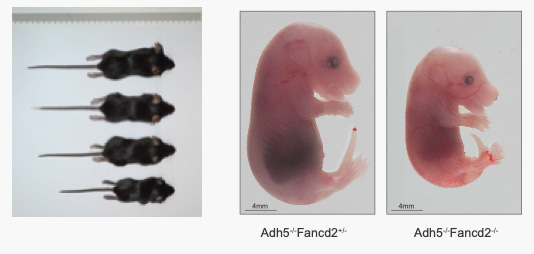
Indeed, the DNA repair and replication defects, and the clinical symptoms of Fanconi Anaemia patients are largely recapitulated in mouse models of Fanconi Anaemia (Fancd2-/-) genetically engineered to accumulate formaldehyde (i.e., Adh5-/- Fancd2-/- double knock out mice), suggesting a novel relationship between the FA syndrome and the formaldehyde metabolism. By a combination of state-of-the-art genetics and molecular biology tools, human cell culture and mouse genetics, we aim to investigate the mechanisms by which cells maintains replication fidelity and chromosome stability, shedding light into the nature of potential endogenous metabolites that inflict DNA damage and stem cell loss.
Research lines:
1-. Molecular mechanisms of Interstrand Crosslink (ICLs) repair: Our work has uncovered endogenously occurring reactive aldehydes as a novel source of ICLs, and how the Fanconi Anaemia DNA repair pathway orchestrates ICL-repair. Cellular metabolic reactions releases vast amounts of highly reactive aldehydes that can potentially damage DNA. We are currently deciphering the molecular mechanisms employed by cells to detect, signal and repair ICLs, by focusing on the identification of new players and the characterization of the molecular mechanisms of replication-associated DNA repair.
2-. Interplay of DNA repair mechanisms during replication fork impairment: During the sensing, signalling and repair ICLs by the ongoing replication fork, several distinct DNA repair pathways such as Fanconi Anaemia, base excision repair (BER), Homologous recombination (HR), non-homologous (NHEJ) or microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ) converge to impaired replication forks to promote error-free repair. However, the pathway choice determining the optimal consecution of repair event is still poorly understood. We are currently examining the role of different repair pathways that functions in collaboration with the Fanconi Anaemia pathway to limit genome instability associated to replication fork defects.
3-. Molecular mechanisms of Interstrand Crosslink (ICLs) repair: Fanconi Anaemia is an ultrarare genetic condition due to mutations in any of the 22 genes identified so far, and mainly characterized by an extreme sensitivity o ICLs, congenital abnormalities, infertility, progressive bone marrow failure and highly elevated risk of cancer. The 22 gene products act in concert in a common cellular pathway to signal and repair endogenous ICLs. Whereas these symptoms are presented in a large proportion of FA patients, mice models deficient in any FA gene do not ed many of these features, unless any of the aldehyde detoxification system (Aldh2 or Adh5) is ablated in combination with FA. By using the best FA mouse model so far described in the literature (Fancd2-/- Adh5-/-) , we are currently investigating novel therapeutic approaches to suppress hematopoietic stem cell loss, bone marrow failure and the cancer predisposition seen in these mouse model.
If you are a highly motivated student or researcher and would like to join us, please contact us at ivrosado@us.es

Miembros actuales
Contacto
Email: contacto@cabimer.es
Web: https://cabimer.sombradoble.es
